Acute coronary syndrome (ACS) is one of the most common health problems globally and a leading cause of death and signficiant morbidity in developed countries. It represents a clinical condition characterised by rapidly developing critical myocardial ischaemia. ACS encompasses three related but distinct clinical entities – unstable angina, non-ST-segment elevation MI (NSTEMI), and ST-segment elevation MI (STEMI).
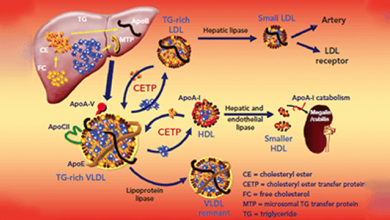
Acute coronary syndromes are characterised by vascular inflammation, subsequent endothelial dysfunction and platelet activation, followed by thrombus formation. Uncontrolled thrombosis can culminate in complete vascular occlusion and STEMI.
Key diagnostic procedures for detection of patients with ACS are ECG at rest and markers of myocardial necrosis. Optical coherence tomography can be used to assess patients with ACS and is useful because it can detect plaques at high risk of rupture and provide additional information about plaque composition, thrombi and collagen. Troponin T and troponin I are specific cardiac markers for myocardial injury and diagnosing the myocardial necrosis.
Management of ACS should encompass both acute and long-term strategies.
What is Myocardial Infarction?
Also known as a heart attack, myocardial infarction (MI) is a necrosis of the heart muscle that originates from an acute obstruction of a coronary artery. It decreases blood flow and leads to irreversible damage to the heart due to myocardial ischaemia.